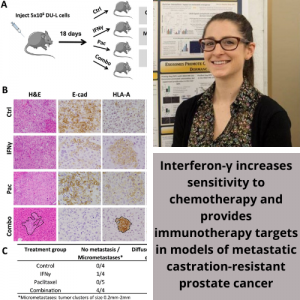
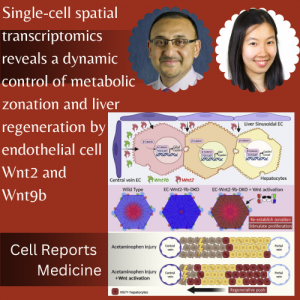
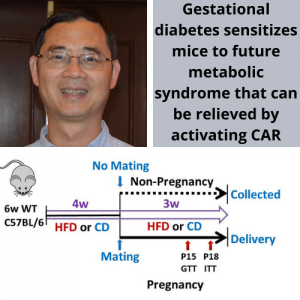
Pictured left to right: D Yimlamai, A Singhi
Mooring M, Fowl BH, Lum SZC, Liu Y, Yao K, Softic S, Kirchner R, Bernstein A, Singhi AD, Jay DG, Kahn CR, Camargo FD, Yimlamai D. Hepatocyte Stress Increases Expression of YAP and TAZ in Hepatocytes to Promote Parenchymal Inflammation and Fibrosis. Hepatology. 2019 Sep 10. doi: 10.1002/hep.30928. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 31505040
ABSTRACT
Activated hepatocytes are hypothesized to be a major source of signals that drive cirrhosis, but the biochemical pathways that convert hepatocytes into such a state are unclear. We examined the role of the Hippo pathway transcriptional coactivators, YAP/TAZ in hepatocytes to facilitate cell-cell interactions that stimulate liver inflammation and fibrosis. Using a variety of genetic, metabolic and liver injury models in mice, we manipulated Hippo signaling in hepatocytes and examined its effects in non-parenchymal cells to promote liver inflammation and fibrosis. YAP expressing hepatocytes rapidly and potently activate the expression of proteins that promote fibrosis (COL1A1, TIMP1, PDGFc, TGFβ2) and inflammation (TNF, IL1β). They stimulate expansion of myofibroblasts and immune cells followed by aggressive liver fibrosis. In contrast, hepatocyte-specific YAP and YAP/TAZ knockouts exhibit limited myofibroblast expansion, less inflammation, and decreased fibrosis after carbon tetrachloride injury despite a similar degree of necrosis as controls. We identified CYR61 as a chemokine that is upregulated by hepatocytes during liver injury but is expressed at significantly lower levels in mice with hepatocyte-specific deletion of YAP or TAZ. Gain and loss of function experiments with CYR61 in vivo point to it being a key chemokine controlling liver fibrosis and inflammation in the context of YAP/TAZ. There is a direct correlation between levels of YAP/TAZ and CYR61 in liver tissues of high-grade NASH patients. CONCLUSION: Liver injury in mice and humans increases levels of YAP/TAZ/CYR61 in hepatocytes, thus attracting macrophages to the liver to promote inflammation and fibrosis.
For full text, please click here.